| |||||||
Europe
North AmericaSouth AmericaAsiaAustralia and OceaniaAfrica |
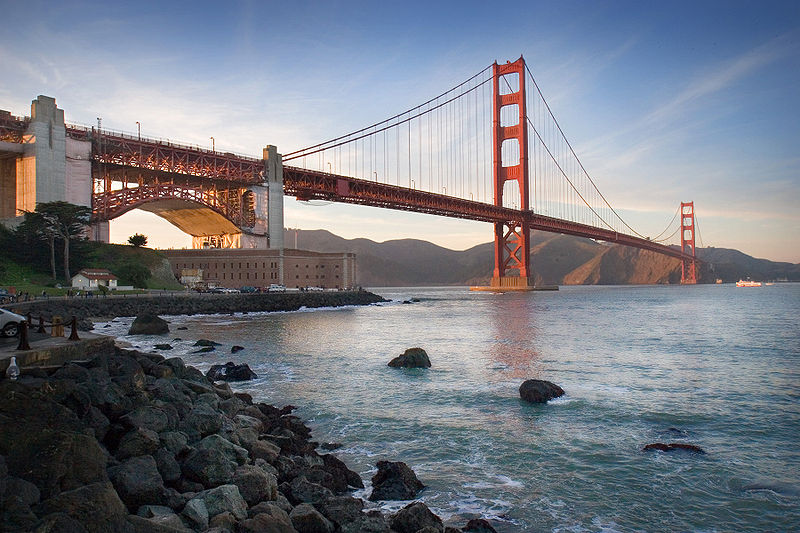
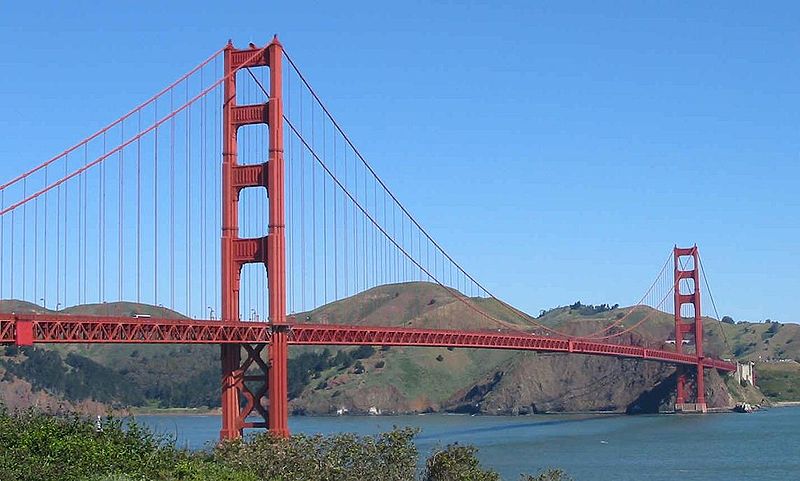
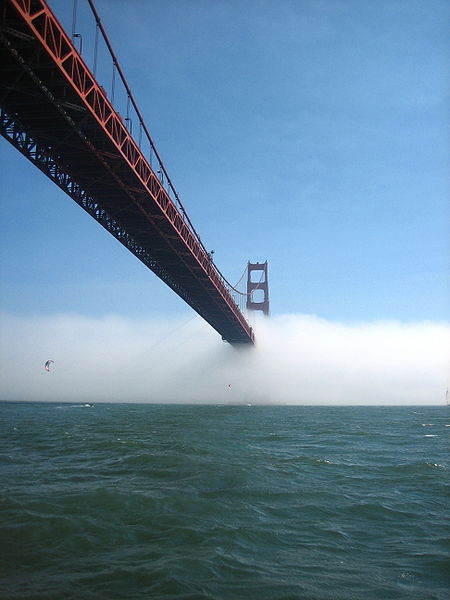
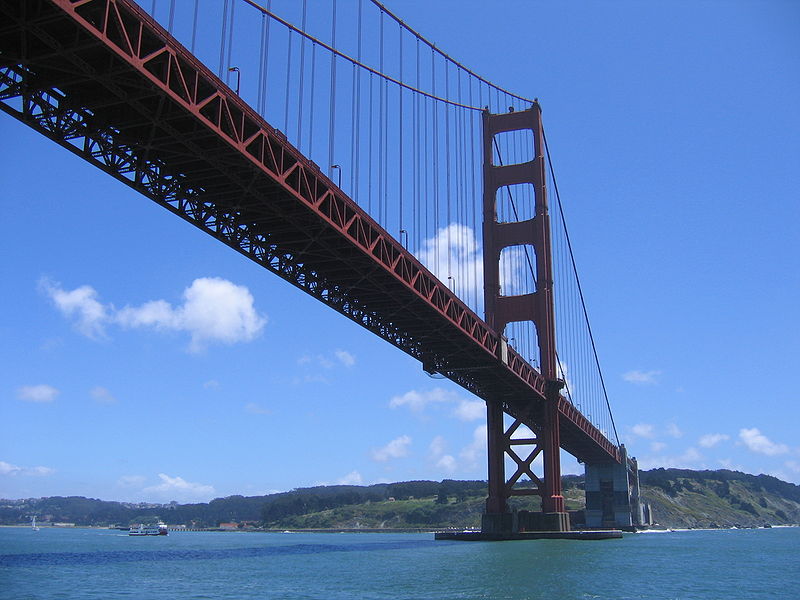
Смотрите также: Golden Gate Bridge The Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge spanning the Golden Gate, the opening of the San Francisco Bay onto the Pacific Ocean. As part of both U.S. Route 101 and State Route 1, it connects the city of San Francisco on the northern tip of the San Francisco Peninsula to Marin County. The Golden Gate Bridge was the longest suspension bridge span in the world when it was completed during the year 1937, and has become an internationally recognized symbol of San Francisco and California. Since its completion, the span length has been surpassed by eight other bridges. It still has the second longest suspension bridge main span in the United States, after the Verrazano-Narrows Bridge in New York City. In 2007, it was ranked fifth on the List of America's Favorite Architecture by the American Institute of Architects.
Golden Gate Bridge Carries 6 lanes of pedestrians and bicycles Crosses Golden Gate Locale San Francisco, California and Marin County, California Design Suspension, truss arch & truss causeways Longest span 4,200 feet (1,280 m) Total length 8,981 feet (2,737 m) Width 90 feet (27 m) Height 746 feet (227 m) Vertical clearance 14 feet (4.3 m) at toll gates, higher truck loads possible Clearance below 220 feet (67 m) at mean higher high water Opening date 27 May 1937
History Before the bridge was built, the only practical short route between San Francisco and what is now Marin County was by boat across a section of San Francisco Bay. Ferry service began as early as 1820, with regularly scheduled service beginning in the 1840s for purposes of transporting water to San Francisco. The Sausalito Land and Ferry Company service, launched in 1867, eventually became the Golden Gate Ferry Company, a Southern Pacific Railroad subsidiary, the largest ferry operation in the world by the late 1920s. Once for railroad passengers and customers only, Southern Pacific's automobile ferries became very profitable and important to the regional economy. The ferry crossing between the Hyde Street Pier in San Francisco and Sausalito in Marin County took approximately 20 minutes and cost US$1.00 per vehicle, a price later reduced to compete with the new bridge. The trip from the Ferry Building took 27 minutes. Many wanted to build a bridge to connect San Francisco to Marin County. San Francisco was the largest American city still served primarily by ferry boats. Because it did not have a permanent link with communities around the bay, the city’s growth rate was below the national average. Many experts said that a bridge couldn’t be built across the 6,700 ft (2,042 m) strait. It had strong, swirling tides and currents, with water 335 ft (102 m) in depth at the center of the channel, and almost constant winds of 60 mph (97 km/h). Experts said that ferocious winds and blinding fogs would prevent construction and operation.
Conception Although the idea of a bridge spanning the Golden Gate was not new, the proposal that eventually took root was made in a 1916 San Francisco Bulletin article by former engineering student James Wilkins. San Francisco's City Engineer estimated the cost at $100 million, impractical for the time, and fielded the question to bridge engineers of whether it could be built for less. One who responded, Joseph Strauss, was an ambitious but dreamy engineer and poet who had, for his graduate thesis, designed a 55-mile (89 km) long railroad bridge across the Bering Strait. At the time, Strauss had completed some 400 drawbridges—most of which were inland—and nothing on the scale of the new project. Strauss's initial drawings were for a massive cantilever on each side of the strait, connected by a central suspension segment, which Strauss promised could be built for $17 million. Local authorities agreed to proceed only on the assurance that Strauss alter the design and accept input from several consulting project experts. A suspension-bridge design was considered the most practical, because of recent advances in metallurgy.
Strauss spent more than a decade drumming up support in Northern California. The bridge faced opposition, including litigation, from many sources. The Department of War was concerned that the bridge would interfere with ship traffic. Unions demanded guarantees that local workers would be favored for construction jobs. Southern Pacific Railroad, one of the most powerful business interests in California, opposed the bridge as competition to its ferry fleet and filed a lawsuit against the project, leading to a mass boycott of the ferry service. In May 1924, Colonel Herbert Deakyne held the second hearing on the Bridge on behalf of the Secretary of War in a request to use Federal land for construction. Deakyne, on behalf of the Secretary of War, approved the transfer of land needed for the bridge structure and leading roads to the "Bridging the Golden Gate Association" and both San Francisco County and Marin County, pending further bridge plans by Strauss. Another ally was the fledgling automobile industry, which supported the development of roads and bridges to increase demand for automobiles. The bridge earned its name, Golden Gate Bridge, after a mention of it in 1927 by San Francisco city engineer Michael O'Shaughnessy. Design Strauss was chief engineer in charge of overall design and construction of the bridge project. However, because he had little understanding or experience with cable-suspension designs, responsibility for much of the engineering and architecture fell on other experts.
Irving Morrow, a relatively unknown residential architect, designed the overall shape of the bridge towers, the lighting scheme, and Art Deco elements such as the streetlights, railing, and walkways. The famous International Orange color was originally used as a sealant for the bridge. Many locals persuaded Morrow to paint the bridge in the vibrant orange color instead of the standard silver or gray, and the color has been kept ever since. Senior engineer Charles Alton Ellis, collaborating remotely with famed bridge designer Leon Moisseiff, was the principal engineer of the project. Moisseiff produced the basic structural design, introducing his "deflection theory" by which a thin, flexible roadway would flex in the wind, greatly reducing stress by transmitting forces via suspension cables to the bridge towers. Although the Golden Gate Bridge design has proved sound, a later Moisseiff design, the original Tacoma Narrows Bridge, collapsed in a strong windstorm soon after it was completed, because of an unexpected aeroelastic flutter. Ellis was a Greek scholar and mathematician who became a University of Illinois professor of engineering despite having no engineering degree. He became an expert in structural design, writing the standard textbook of the time. Ellis did much of the technical and theoretical work that built the bridge, but he received none of the credit in his lifetime. In November 1931, Strauss fired Ellis and replaced him with a former subordinate, Clifford Paine, ostensibly for wasting too much money sending telegrams back and forth to Moisseiff. Ellis, obsessed with the project and unable to find work elsewhere during the Depression, continued working 70 hours per week on an unpaid basis, eventually turning in ten volumes of hand calculations. With an eye toward self-promotion and posterity, Strauss downplayed the contributions of his collaborators who, despite receiving little recognition or compensation, are largely responsible for the final form of the bridge. He succeeded in having himself credited as the person most responsible for the design and vision of the bridge. Only much later were the contributions of the others on the design team properly appreciated. In May 2007, the Golden Gate Bridge district issued a formal report on 70 years of stewardship of the famous bridge and decided to right an old wrong by giving Ellis major credit for the design of the bridge. Comments: 0 |
|
|||||